Nose-to-brain delivery allows application of drugs at the roof of the nasal cavity, which are transported to the central nervous system (CNS) of humans (A) and rodents (B).
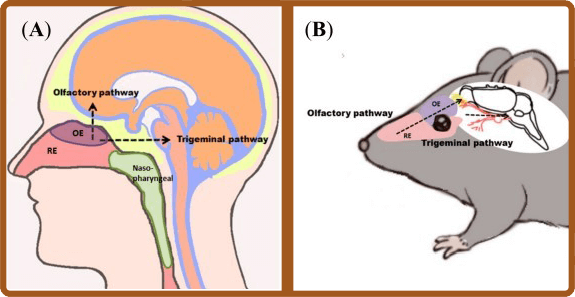
Nose-to-brain transport can either be mediated via the olfactory or the trigeminal pathway. Drugs passing along the olfactory pathway target the olfactory bulb, whereas drugs transported via the trigeminal pathway are delivered predominantly to the brain stem.
- Blood-brain barrier and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier are major obstacles in CNS drug delivery, since they block most molecules from entering the brain.
- Nose-to-brain delivery is a minimally invasive drug administration pathway, which bypasses the blood-brain barrier as the drug is directed from the nasal cavity to the brain.


